Diversity in web design means having humans with many specific backgrounds, cultures, and lifestyles experiences running together to create websites. It’s about building teams which are a mix of different styles of human beings – different races, genders, ages, skills, religions, and approaches of questioning and searching at the world. Not everyone comes from the identical vicinity or has had the equal upbringing.
Having this variety and range wide, the websites get constructed with many distinctive views worried. The websites become being greater inclusive and relatable to all the exclusive types of human beings that may use them. A numerous net layout group can higher recognise and account for the needs of a numerous range of users and audiences. Different viewpoints lead to extra creative and revolutionary internet site answers.
Why is diversity important in web design?
Diversity is important because it means all the different people feel valued and included. They feel like they are a part of the team and are respected, no matter their background. Everyone’s specific stories and views are seen as something fantastic that makes the crew stronger. The aim is to create groups and businesses wherein human beings do not all come from the equal mildew. There are many distinctive voices, viewpoints, and capabilities represented. This variety helps make higher websites and on-line experiences for all the special customers out there.
Diversity in web layout groups may be immediately related to making internet content material more available. When web design teams lack range, there’s a higher threat that the wishes of sure person organisations can be neglected or no longer absolutely understood. For example: If the group has no one with a disability, accessibility troubles for users with disabilities may additionally get ignored. If the team is all younger, they will not recollect the wishes of older users with vision/mobility barriers. If the group is culturally homogenous, they will lay out with subconscious biases that make the content material less accessible to different cultures.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines are a hard and fast of policies created via the Web Accessibility Initiative of the World Wide Web Consortium to ensure websites are on hand to human beings with disabilities. These pointers provide internet designers and builders with pointers and first-class practices for making the content that makes up websites – which includes textual content, snapshots, movies, forms, and code – usable for individuals with a numerous variety of abilities. There are a few crucial rules and suggestions for making websites on hand to anyone, including people with disabilities. These rules are known as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
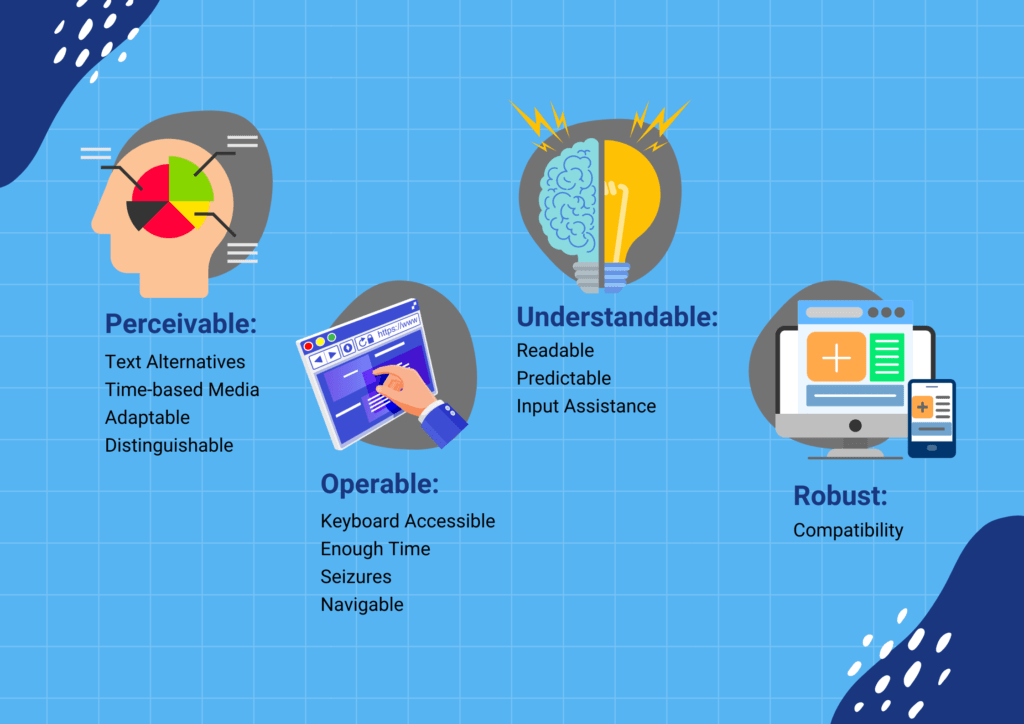
P.O.U.R. Principles of Accessibility
The WCAG says there are four foremost ideas that websites have to comply with to be reachable:
1. Perceivable – This manner the content and interface on the internet site must be presentable in ways that all customers can perceive and sense, whether they can see, listen, or understand in different methods.
2. Operable – The internet site’s parts, navigation, and controls should be operable and usable by using all and sundry. Users have to be able to interact and operate the site’s capabilities through voice, keyboard, or assistive gadgets if wanted.
3. Understandable – The content, operations, and commands on the internet site want to be comprehensible. The language and layout have to be clean and logical for all users to realise.
4. Robust – The code at the back of the internet site ought to be sturdy sufficient that it could be accessed reliably by way of a huge form of user equipment, technology, and assistive gadgets now and within the future.
Ways to improve Web Content Accessibility
1. Structure and arrange with headers:
Headers assist to separate and label extraordinary sections of content on a website. Using right header tags makes it less difficult for people in the usage of display readers to navigate the page. Headers offer an outline showing what statistics is contained in each phase.
2. Assign alt tags for photos:
Alt tags are text descriptions for snapshots on an internet site. People who are blind or have low imaginative and prescient rely upon display readers to study out these alt textual content descriptions. Writing clean and correct alt textual content guarantees images are available to these customers.
3. Use descriptive name for hyperlinks:
Instead of using indistinct terms like “click on here”, hyperlink text ought to without a doubt describe the hyperlink’s vacation spot. Descriptive links allow all customers, consisting of those in the use of display screen readers, to effortlessly understand wherein each link is going.
4. Use colouring carefully:
Colours need to never be the handiest way to deliver critical facts on an internet site. People with shade blindness can also have hassle perceiving colour variations or contrasts. Textual cues and patterns need to accompany colour coding.
5. Design forms for net accessibility:
Forms are an essential component of many websites, permitting users to input data and have interaction with on-line services. However, poorly designed bureaucracy can create widespread barriers for customers with disabilities. Any uncommon necessities or formatting guidelines need to be truly stated with commands provided. Proper markup, which includes the usage of suitable HTML tags and ARIA attributes, is important for ensuring that shape elements are introduced and interpreted efficiently by means of assistive technologies.
6. Use tables for tabular information:
Tables are effective tools for presenting statistics in a structured grid format, but they need to be used judiciously and handiest for his or her intended motive – displaying tabular information. Using tables for layout purposes, along with positioning factors on a website, can create huge confusion for customers relying on display screen readers and different assistive technologies.
7. Ensure website on-line navigation thru a keyboard:
Many people with disabilities, inclusive of those with motor impairments or visual impairments, might also want to navigate the usage of best a keyboard. Websites should be designed and coded with keyboard accessibility in thoughts, ensuring that everyone interactive elements can be reached and activated in the usage of keyboard commands and tab order. This method now not handiest incorporates users with disabilities, but additionally advantages users who prefer or want to navigate the usage of keyboard shortcuts for elevated efficiency.
8. Turn dynamic content material into one hand content material:
Dynamic content material, which includes interactive menus, pop-ups, or content material that updates without a web page refresh, may not be perceivable or operable by way of assistive technology like display screen readers if accessibility standards are not accompanied. To make certain that dynamic content stays handy, net builders need to adhere to accessibility guidelines and fine practices when coding and enforcing these interactive factors.
Conclusion:
Making websites truly available requires cautious attention and implementation of accessibility fine practices at some point of the design and improvement system. By following recommendations like structuring content material with right headings, presenting descriptive alt textual content for images, the usage of clear link labels, ensuring coloration contrast, optimising paperwork and tables, enabling keyboard navigation, and making dynamic content material on hand, websites can grow to be usable for all of us no matter disabilities.
Improve your brand with VMA Graphic Design & Print! From branding and printing to logo design, website design, and marketing graphic design, our expert team is here to support you 24/7. Contact us today to ensure your projects are inclusive, accessible, and impactful.
You may also like:
The Art of Minimalist Website Design
Decoding the History and Impact of Graphic Design
Helpful Source:


